详情
Aviation fuel designed for use in aircraft powered by gas-turbine
engines. It is colorless
to straw-colored in appearance. The most commonly used fuels for
commercial aviation are Jet
A and Jet A*1, which are produced to a standardized international
specification. The only other
jet fuel commonly used in civilian turbine-engine powered aviation
is Jet B, which is used for its
enhanced cold-weather performance.
Jet fuel is a mixture of a large number of different hydrocarbons.
The range of their sizes
(molecular weights or carbon numbers) is restricted by the
requirements for the product, for
example, the freezing point or smoke point.Kerosene-type jet fuel
(including Jet A and Jet A*1)
has a carbon number distribution between about 8 and *6 (carbon
atoms per molecule); wide-cut
or naphtha-type jet fuel (including Jet B), between about 5 and
*5.
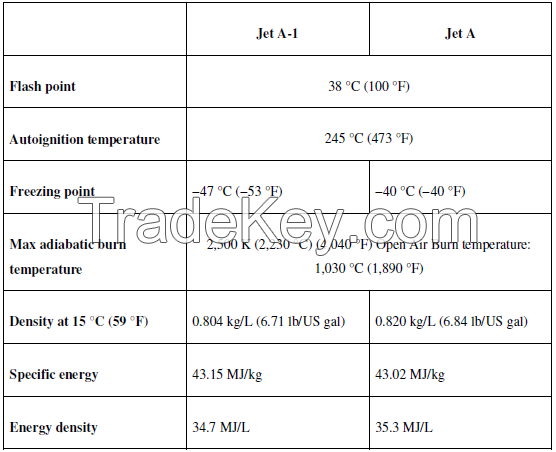
6.1 Differentiation between Jet A and Jet A 1